What is diabetic neuropathy?
Diabetic neuropathy is a common and serious complication of diabetes. Uncontrolled high blood sugar levels can harm your nerves. That damage is called neuropathy. It can happen in several ways, but in most cases, neuropathy leads to health problems. Between 60–70% of people who have diabetes get some forms of neuropathy. That’s why it is crucial to check your blood sugar levels regularly and talk to your doctor if you spot any signs of neuropathy.

Types of diabetes neuropathy
There are four main types of diabetic neuropathy. A person may get just one type or signs of several types. Most of the problems develop very gradually, so you may not notice neuropathy until visible damage has occurred. The symptoms and signs of neuropathy may vary widely, depending on what nerves are affected.
Peripheral neuropathy typically affects the feet and legs. In rare cases, it may involve the arms, back, and abdomen. The symptoms of peripheral neuropathy are the following: numbness, burning (especially in the evening), and tingling.
If you notice any of these signs, consult with your doctor to avoid dangerous health issues. The condition usually gets better when your blood sugar is under control. To prevent peripheral neuropathy, check your legs and feet on a daily basis, use moisture cream if they are dry, take care of the toenails, and wear comfortable shoes.
Autonomic neuropathy usually causes problems with digestive system. It also may affect the stomach, sometimes the urinary system and blood vessels. When autonomic neuropathy involves digestive system, it results in bloating, diarrhea, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, or constipation. See your doctor to get medication to relieve the symptoms. Smaller meals may also help to feel better.
In blood vessels, autonomic neuropathy can manifest itself through increased heart rate, low blood pressure, nausea, dizziness, or loss of consciousness when standing up too quickly. If you have this condition, don’t be too quick while standing up. You may also need to take certain medication.
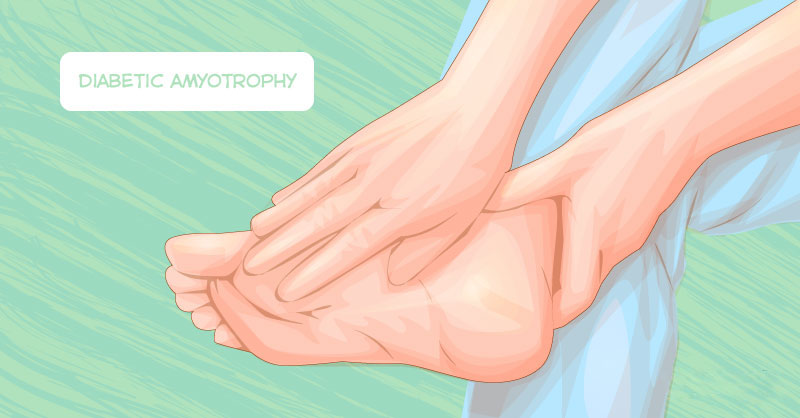
Proximal neuropathy leads to pain (often on one side) in the thighs, hips, or buttocks. This type of neuropathy can also lead to leg weakness.
People with this condition need treatment. Luckily, physical therapy and meds can help to improve the symptoms.
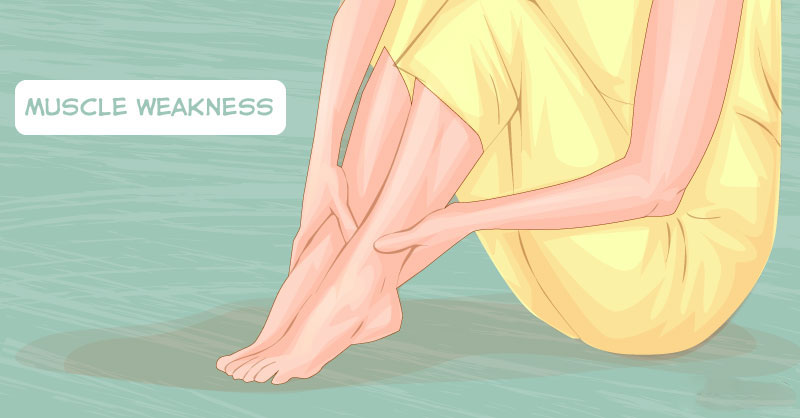
Focal neuropathy develops suddenly and affects certain nerves typically in the head, legs, or torso. It usually comes with pain and muscle weakness.
What can help to prevent diabetic neuropathy?
Some measures may lower the risk. They include the following:
— control your blood pressure;
— make healthy food choices;
— be physically active;
— quit smoking.
People with diabetes can help prevent or delay diabetic neuropathy by keeping the blood sugar levels well-controlled, taking care of their feet, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.