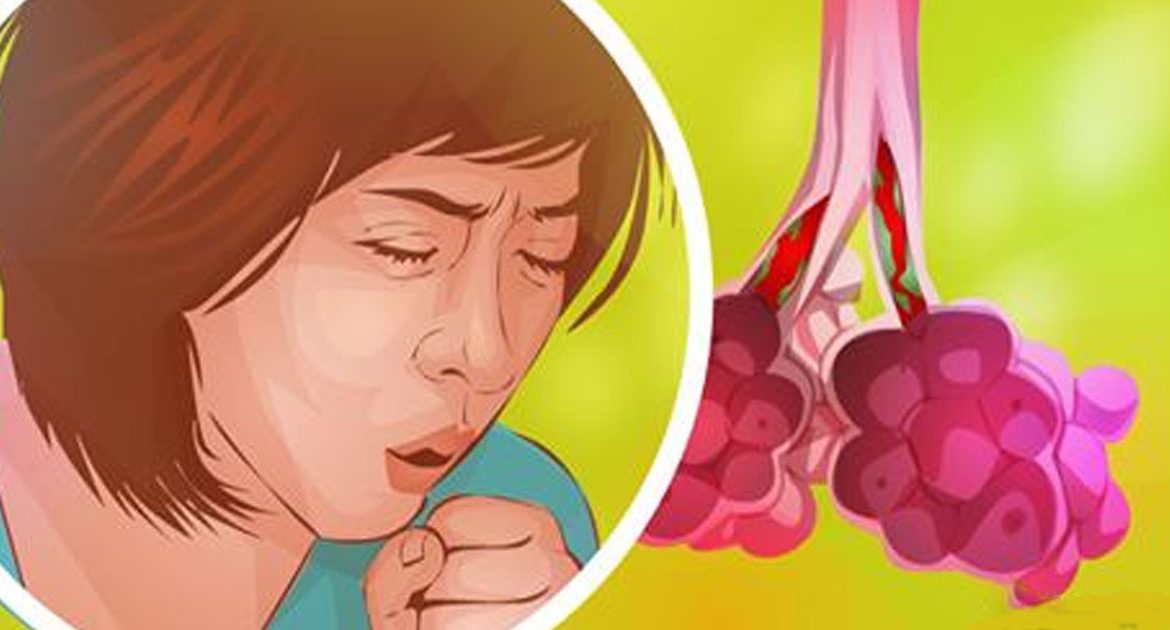
A common cold or the flu usually relieves in several weeks, but in some cases, you may develop bronchitis. Generally, bronchitis means an inflammation of the bronchial tubes that pass through the lungs and carry air. This condition is usually accompanied by a large amount of a mucus and a nagging cough.
Types of bronchitis
Doctors distinguish two types of bronchitis:
- Acute bronchitis. It is the more common one, and its symptoms usually last several weeks. Acute bronchitis typically doesn’t cause further health problems.
- Chronic bronchitis. This type is more serious, because it may come back. Chronic bronchitis plays a role in developing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
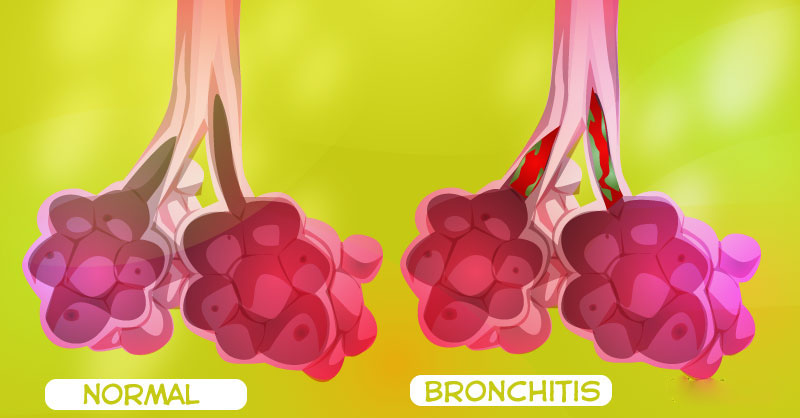
Causes of bronchitis
Bronchitis can be a result of exposure to the viruses, bacteria, and certain other irritant factors. Acute bronchitis is caused by viruses that also cause colds and flu. Repeated irritations of airway tissues usually lead to chronic bronchitis. Chronic bronchitis may develop after episodes of acute bronchitis and long-term exposure to air pollution. Moreover, one of the most common causes of chronic bronchitis is cigarette smoking.
Common symptoms of bronchitis
The symptoms of acute or chronic bronchitis may include the following:
- Cough.
- Excessive production of mucus that can be clear, white or yellowish color.
- Shortness of breath.
- Fatigue.
- Fever and chills.
- Chest congestion.
- Wheezing or whistling sounds when you breathe.

If you develop acute bronchitis, you may have cold symptoms, including body aches and a headache. While almost all symptoms normally improve in about a week, you may experience a nagging cough for several weeks. Chronic bronchitis lasts three months minimum and often recurs.
Bronchitis can result in serious complications. The most common one is pneumonia when the infection involves the lungs. About 5% people with bronchitis develop pneumonia. The risk factors for pneumonia include:
- Age: it typically occurs in older adults.
- Smoking: smokers are at greater risk.
- Health conditions: people with other diseases and a weakened immune system are more likely to develop pneumonia.
When to visit a doctor
Sometimes bronchitis can lead to severe health problems, so see your doctor if:
- you cough more than three weeks;
- cough keeps you awake;
- you experience fever higher than 100.4 F;
- you notice discolored mucus or blood;
- cough is followed by shortness of breath;
- cough causes chest pain.

How to prevent bronchitis
Here are certain ways to decrease your chances of developing bronchitis.
- Quit smoking. Cigarette smoking significantly increases your risk of chronic bronchitis.
- Get the flu vaccine. In many cases, viruses cause acute bronchitis, and a flu vaccine can protect you from getting the flu. Vaccination may also prevent some types of pneumonia.
- Wash your hands frequently. Washing your hands reduces your risk of catching viral infections. You may also apply alcohol-based hand sanitizers.
- Wear a mask. Protect your lungs from dust and fumes at work.
Bronchitis is a serious condition, but if you start your treatment in time, you will be able to back to a normal, healthy life very soon.