Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most frequently occurring form of skin cancer. It involves the basal cells – a type of cells in your skin that produces new skin cells when old ones die off. Basal cell carcinoma often manifests itself as a slightly transparent bump, but it can take other forms too. Basal cell carcinoma usually affects the areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun, for example, head or neck.
Doctors believe that most basal cell carcinomas are caused by long-term exposure to ultraviolet radiation from sunlight. That’s why protecting your skin from the sun can help prevent this condition. BCC almost never metastasizes beyond its original site. But it doesn’t mean that it shouldn’t be taken seriously: without proper treatment, BCC can be disfiguring.
More than 4 million cases of basal cell carcinoma are diagnosed in the United States each year, so it is very important to know more about its detection, risk factors, and prevention.
Symptoms
Basal cell carcinoma usually appears as a change in the skin that can look different. You may notice a skin growth with blood vessels in it or something like a small “pearly” bump.
Here are the warning signs of BCC to pay attention to.
1. An open sore
An open sore that bleeds from time to time and doesn’t heal up for several weeks is a very common symptom of an early BCC.
2. A reddish patch or irritated area
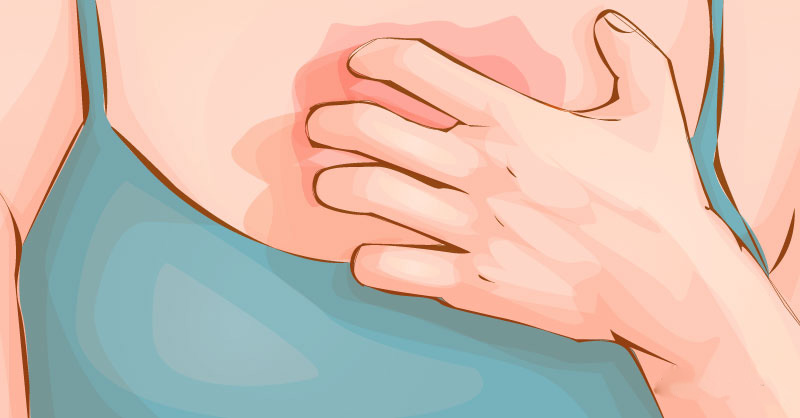
BCC can look like a reddish spot, frequently appearing on the face, chest, arms, or legs. Sometimes, the patch may crust, itch, or hurt. At other time, it doesn’t cause discomfort.
3. A shiny bump or nodule
BCC may come up like a small “pearly” or clear bump that is easily confused with a normal mole. It can vary widely in color, including pink, red, white, tan, black, or brown, especially in dark-haired people.
4. A pink growth
Basal cell cancer can appear as a pink growth with a slightly elevated border. This lesion often enlarges slowly and small blood vessels can show up on the surface.
5. A scar-like lesion
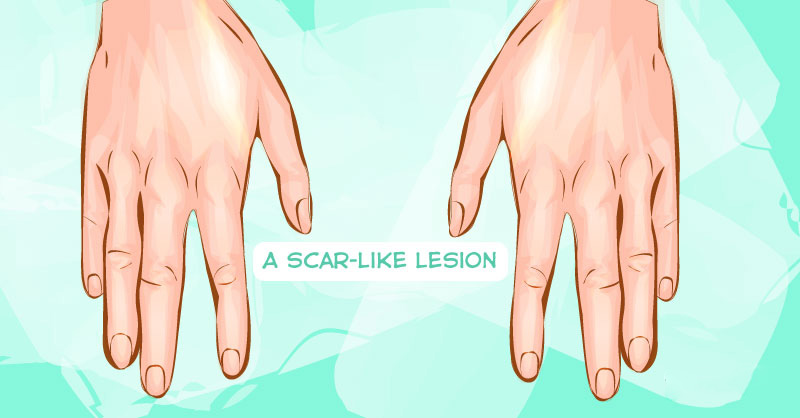
A white, waxy, scar-like area without a clear border is the least common sign of BCC. This lesion is easy to overlook, but it usually indicates the presence of an invasive BCC. It means that the tumor is larger than it is on the surface.
In some cases, BCC can resemble other skin condition, such as psoriasis or eczema. That’s why only a trained doctor can decide for sure. If you notice any of the warning signs, consult your physician as soon as possible.
Basal cell carcinomas are easily treated in their early stages.
What to do to prevent basal cell carcinoma
You may lower the risk of this condition if you:
1. Avoid the midday sun
Doctors advise to avoid the sun when its rays are the strongest. For most places, it is the period between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Because the sun’s rays are most harmful at this time, try to plan outdoor activities for other times of the day. You should follow this rule even in winter because your skin absorbs UV radiation year-round.
2. Use sunscreen
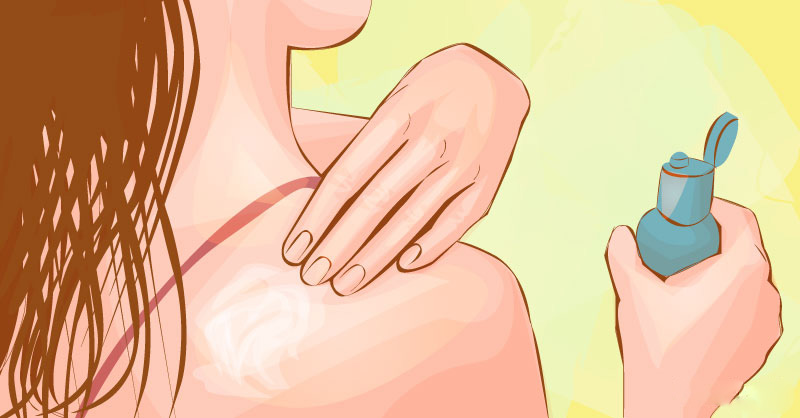
According to the dermatologists, it is necessary to choose a sunscreen that blocks both UVA and UVB types of radiation and has an SPF of minimum 15. Apply sunscreen when you are outside and reapply every two hours or even more frequently if you are swimming. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends using broad-spectrum sunscreens with an SPF of 30 and higher.
3. Avoid tanning
Tanning beds give off UV radiation that increases the risk of skin cancer.
4. Be familiar with your skin to notice changes in time
Monitor your skin condition to know what your skin normally looks like. If you find something unusual, talk to your doctor.





