“The human body is the best work of art.” ― Jess C. Scott
Few things are as complex and interesting to us as our own bodies. We each only have one, and it’s supported by thousands of parts working in unison. Understanding the pieces that make us who we are and how they work together is cool! Here are our favourite 40 facts about the human body!
50. Who shed all over the carpet?
Humans shed about 600,000 particles of skin every hour. In fact, most of the dust underneath your bed is probably your own dead skin.

49. Baby bones.
A human baby has 99 more bones than an adult. A baby’s skeleton is mostly made up of cartilage. As a person grows up, most of this cartilage turns into bone in a process called ossification, and the ossification process results in the joining of certain bones. Consequently, new born babies have around 305 bones, while an adult has just 206 bones.

48. A few small pieces.
An adult human being is made of approximately 7,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 atoms. Obviously, this varies based on the size of the person and their body composition.

47. Pumping the distance.
There are 100,000 miles of blood vessels in an adult human body. The largest blood vessel is the aorta, which is just over an inch in diameter.
46. Our awesome noses.
Researchers estimate that the average human being can distinguish between 1 trillion different odors. This is much more acute than the human eye, which can distinguish about 10 million different colors.

45. Swimming in spit.
In a lifetime, an average person produces about 25,000 quarts of saliva, enough to fill two swimming pools. We also produce about a litre of mucus per day.

44. It lives in you.
Your body has enough iron in it to forge a 3-inches-long nail. You also have enough sulfur to kill all fleas on an average dog, enough carbon to make 900 pencils, enough potassium to fire a toy cannon, enough fat to make 7 bars of soap, enough phosphorous to make 2,200 match heads, and enough water to fill a ten-gallon tank.

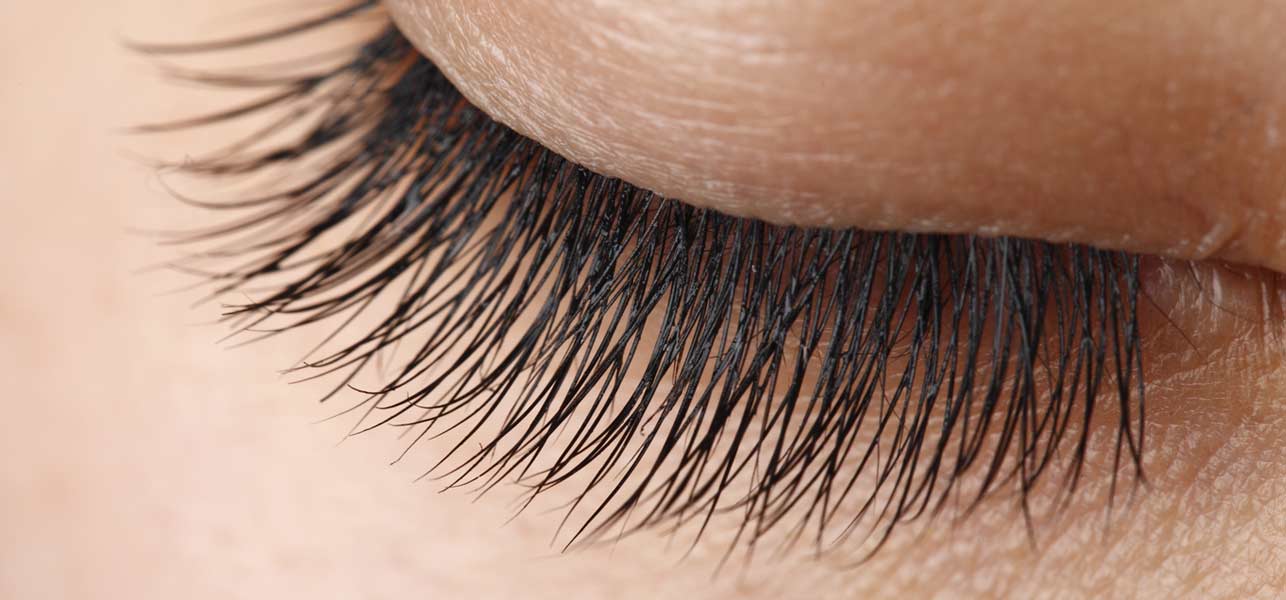
43. Close your eyes.
We all have tiny mites living in our eyelashes. These little mites actually aren’t too choosey; they’ll live anywhere as long as they have access hair follicles. They’re found on other parts of the body and on a host of other mammals.

42. The strongest muscle.
Pound for pound, the strongest muscle in the human body is the masseter (jaw muscle). It can clamp your chompers shut with 55 pounds of force on the incisors and 200 pounds of force on the molars.

41. Stinky humans.
Sweat itself is odorless. It’s the bacteria on the skin that mingles with it and produces body odor. Bacteria that are naturally present on our skin thrive in sweaty regions.

40. Growing strong.
Your ears and nose will never stop growing until the day you die. In fact, your earlobes will also elongate from gravity.

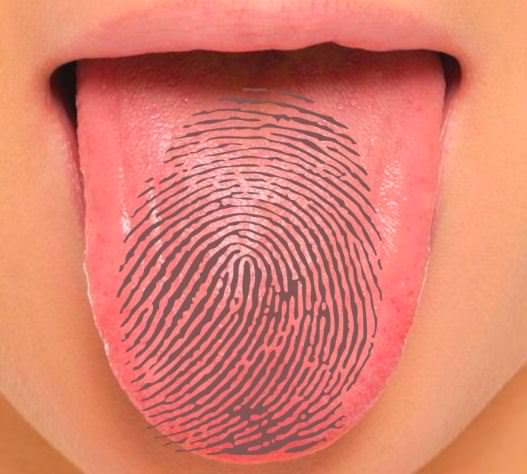
39. Don’t lick the gun.
Similar to fingerprints, everyone also has a unique tongue print. It may be some time before your local police station starts taking tongue prints, but research on the required 3-D imaging technology is already being developed and tested.

38. Strength if steel.
Ounce for ounce, human bones are stronger than steel. A cubic inch of bone can bear a load of 19,000 lbs.—roughly the weight of five pickup trucks.
37. Booze and blue.
People with blue eyes have a higher alcohol tolerance. Interestingly, they also have higher rates of alcohol abuse and dependency.

36. Better sight than your iPhone.
If the human eye was a digital camera it would have 576 megapixels. Currently, the most expensive digital camera in the world has 200 megapixels.

35. Carrying some friends with you…
All of the bacteria in our body collectively weighs about 4 pounds. That’s enough to fill a big soup can. In fact, there are more bacteria in your mouth than there are people in the world.
34. Move to the music!
In some cardiovascular units, slow and quiet music is used to relax the patients and lower their blood pressure and heart rate.

33. Brain power.
Your brain accounts for only 2% of your body weight, yet it uses 20% of the total oxygen and blood in your body.

32. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
If uncoiled, the DNA in all of your body’s cells would stretch 10 billion miles, which is long enough to reach from here to Pluto and back.

31. Eaten from the inside…
Within three days of death, the enzymes that once digested your dinner begin to eat you. Ruptured cells will become food for the bacteria in your gut, which will release enough noxious gas to bloat your body and force your eyes to bulge outward.
30. Supercomputer storage.
In a lifetime, your brain’s long-term memory can hold up to 1 quadrillion (1 million billion) bits of information.

29. The perilous journey of a hot dog.
The gastrointestinal tract is a 30-foot tube that runs from your mouth to your anus. There’s a few moving parts, but a long story short is that food comes in and poop goes out.
28. Barrels of blood.
Your heart will pump about 1.5 million barrels of blood during your lifetime. That’s enough to fill 200 train tank cars.
27. You can’t stop the beat.
As long as it has an oxygen supply, your heart can keep beating even if it’s separated from the body because it has its own electrical impulse.
26. Brain age.
Your brain keeps developing until your late 40s.
25. Sweet cilia.
Our lungs and nasal passages have exquisitely tiny hairs called cilia that can “taste” bitter flavors. They also serve to remove dust and foreign particles from the respiratory tract.
24. You feel me?
Human fingers can feel objects as small as 13 nanometers. This means that if your finger was the size of the Earth, you would feel the difference between houses and cars.

23. A heck of a fever.
The highest recorded body temperature in a human being was a fever of 115.7°F. A fever over 107.5°F is enough to damage the brain and, if untreated, cause death.

22. Touch your heart.
The human heart is not on the left-hand side of the body. It’s in middle of your chest, in between your right and left lung. It is, however, tilted very slightly to the left.
21. Brain genes.
Half of your genes describe the complex design of your brain, with the other half describing the organization of the other 98% of your body.
20. Cell replacement.
Your taste buds are replaced every 10 days. Conversely, the average age of a human fat cell is 10 years.

19. Shave if you want to!
There is no scientific evidence that shaving or waxing will make your hair come back thicker. There are believed to be two reasons that the myth continues to flourish. First, humans just aren’t the best observers. Second, hair often does grow back thicker when people first start to shave, but this isn’t caused by shaving. When an adolescent boy shaves his mustache for the first time, it’s likely to grow back thicker. This isn’t because shaving caused this; it’s because the hormonal changes in his body (which occur regardless of shaving) are encouraging new and thicker facial hair growth.
18. Organ flipping.
1 in 10,000 people has their internal organs reversed or “mirrored” from their normal positions. The condition is called situs inversus.
17. Grasping the strength of your pinky.
Without your pinky finger, you would lose about 50% of your hand strength. While the index and middle fingers function with the thumb in pinching and grabbing, it’s the pinkie that teams up with the ring finger to provide grip power.

16. Keeping cool down there.
Men’s Testicles hang between the legs to keep cool because sperm dies at body temperature. Keeping those baby-makers cool is a top priority, so make sure to keep your laptop off those bad boys!

15. Extra bones.
1 person out of every 200 people has an extra rib.

She likely doesn’t have extra ribs.
14. Keeping up with abrasion.
Your mouth is made of the same skin cells as a vagina. Flattened epithelial cells are well suited to areas in the body subject to constant abrasion, as layers can be sloughed off and replaced before quickly.

13. Cute little muscles.
Muscle comes from the Latin “musculus.” Musculus means “little mouse,” and this was used to describe muscles because biceps were thought to look like mice.

12. Liar, liar, pants on fire!
When telling a lie, people blink less frequently than normal. After the lie is told, they speed up to around eight times faster than usual.

11. Voices and words.
More than 3% of people are born with phonagnosia: they can’t recognize the voices of familiar people. People suffering from phonagnosia do not suffer from aphasia (an inability to comprehend and formulate language), which suggests that separate areas of the brain govern linguistic comprehension and voice recognition.

10. Annoying? Yes. Unhealthy? Maybe not.
A scientist cracked his knuckles on one hand for over 50 years to prove it did not cause Arthritis. After 50 years, he concluded that there was no arthritis in either hand, and no apparent differences between the two hands. This is, of course, a rather small data set, but it’s interesting none the less!

9. Doing it in the morning.
You can burn 20% more fat by exercising in the morning on an empty stomach. Sex burns 3.6 calories a minute, so fifteen minutes of morning sex should burn off 130 calories.

8. Take that, worm brain!
Humans have no more genes than worms. We have less genes than a tomato. How could this be, given that the all-powerful homo sapiens are clearly a more complex species? We’re not sure, but scientist have noted that the number of genes in the genome may be less linked to complexity than we thought.

7. Coughing at the speed of sound.
A strong cough forces air out of the airways at speeds up to 620 mph, which is almost as fast as the speed of sound.

6. Can you hear your mouse scrolling?
Hearing is the fastest human sense. Your brain can recognize a sound 10 times faster than the blink of an eye, in as little as 0.05 seconds.

5. Controversial bras.
Bras make breasts sag. Bras also do not reduce back pain. A leading study found that women who never wore bras had nipples an average of seven millimeters higher each year than regular bra users. Before you go throwing away your bras, note that the benefits of not wearing a bra will only be seen in younger women who are not obese, according to those managing the study.

4. Recovering from the miracle of giving life.
After child birth, a woman’s vaginal muscles can take up to 6 months to get back to their normal shape and size.

3. A green diet.
We can’t digest grass because our bodies don’t have what it takes to break down the cellulose found in the plant. Grass also contains a lot of silica, an abrasive that quickly wears down teeth, so your dentist wouldn’t be thrilled about a grass diet. Grazing animals have teeth that continually grow to replace worn tooth surfaces.

2. Toe to toe.
Your big toe carries more weight than any other toe, bearing about 40% of your body weight. To enlist in the United States army, you need to have all ten toes intact.

1. Evolution stinks!
One prevailing theory as to why butt hair exists is that there’s simply no significant evolutionary pressure against butt hair. I.e. it doesn’t affect our ability to mate, so the random mutations that caused butt hair persisted.
Other theories take a smellier view of things, suggesting that butt hair helps scent communication. We have body hair in the same areas where we produce odors. The hair is there to hold onto oily secretions that have their own smell and are consumed by bacteria that produces even more smells. Early human ancestors used their personal smell to actually help them with everything from broadcasting territorial rights to attracting mates.
Our bodies are both weird and amazing. Liked Video this with your friends by clicking below!