If you are one of the many who have replaced the old-fashioned standard light bulbs with the new, environmentally-friendly, energy saving light bulbs, we must inform you that you have made a huge mistake, unfortunately.
Apparently, these energy saving light bulbs are extremely toxic and pose serious health risks, so the U.S.
Environmental Protection Agency has laid out an emergency protocol to teach us how to act in the case of a bulb breakage, and prevent the harmful effects of the release of the poison gas.
The findings of a study conducted at the Fraunhofer Wilhelm Klauditz Institute for German’s Federal Environment Agency showed that when they have been broken indoors, the energy-saving light bulbs release 20 times the maximum acceptable mercury concentration into the air.
These light bulbs can cause:
- Anxiety
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Migraines
- Cluster headaches
- Seizures
- Inability to concentrate
These light bulbs cause severe health dangers, and these are the three most important things you need to know about them:
Energy— saving light bulbs contain mercury, which is a potent neurotoxin that has disastrous effects on pregnant women and children. It is especially toxic to the kidneys, liver, brain, and the nervous system, and damages the immune, cardiovascular, and reproductive systems. The exposure to mercury causes headaches, memory loss, tremors, anxiety, insomnia, cancer and Alzheimer’s.
Energy Saving Bulbs Emit a Lot of UV Rays
These lamps release UV-B and traces of UV-C radiation, which damages the eyes and leads to skin cancer. Moreover, this radiation directly attacks the immune system, and damages the skin tissues and thus impedes the proper formation of vitamin D-3.
Energy Saving Light Bulbs are Cancer-Linked
Peter Braun at Berlin Germany’s Alab Laboratory conducted a study which revealed that these light bulbs contain 3 known carcinogens, as follows:
Naphthalene – This is a volatile white crystalline compound, a product of the distillation of coal tar, and is used in mothballs and as a raw material for chemical manufacture.
Phenol – This mildly acidic toxic white crystalline solid, is also a product from coal tar and is commonly used in chemical manufacture.
Styrene – This is an unsaturated liquid hydrocarbon, which is obtained as a petroleum byproduct.
Therefore, these are some good reasons to go back to regular incandescent bulbs, aren’t they?
You will undoubtedly prevent dangerous accidents thus, but you should be really careful while doing so, as any breakage will pose extremely serious health risks.
Due to this, the Environmental Protection Agency has created a very detailed protocol which serves to help one deal with the mercury and cancer-linked chemicals in these light bulbs.
In the event of a bulb breakage, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency provides the following emergency procedure guidelines:
Before Cleanup
Your children and pets should leave the room, and you should open a window or a door to air out the room for about 10minutes. You should also shut off the central forced-air heating/air-conditioning system.
You will need the following materials:
- Stiff paper or cardboard
- Damp paper towels or disposable wet wipes
- Sticky tape
- A glass jar with a metal lid or a sealable plastic bag.
During Cleanup
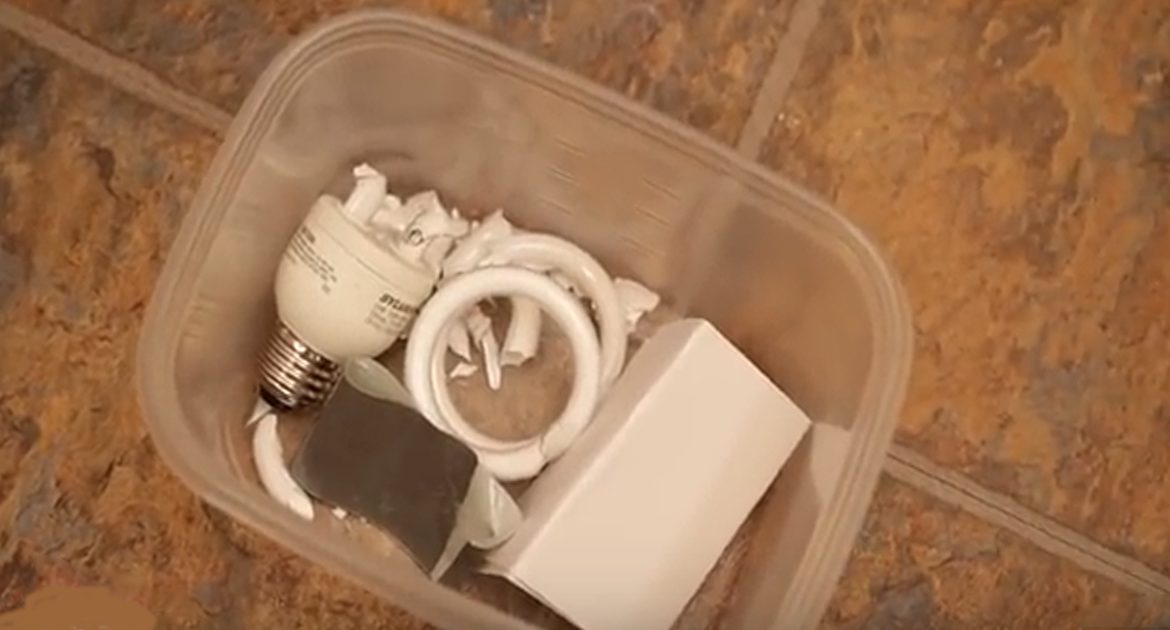
You should collect the broken glass and powder, but do not vacuum, as it might spread mercury-containing powder or mercury vapor. With the stiff paper or cardboard, scoop up the glass fragments and powder, and pick up the smallest remains with the sticky tape.
Then, place it in the glass jar or plastic bag. The cleanup materials should be stored in a sealable container.
After Cleanup
You should air out the room for several hours afterward, with the heating or air conditioning turned off.
Note that you mustn’t leave any bulb pieces or cleanup materials at home. Instead, put all bulb debris and cleanup materials outdoors in a trash container or protected area.
Some localities require citizens to bring the fluorescent bulbs to a local recycling center. If yours does not, dispose of them with the household trash.